Go1.18 调度器-G任务
发表于 · 归类于
代码 · 阅读完需 13 分钟 ·
报告错误 ·
阅读:
编译器将 go func() 翻译为newproc调用,目标函数及其参数被打包成funcval结构对象。
// main.go
func test(x int, p *int) {
println(x, *p)
}
func main() {
x := 111
y := 222
go test(x, &y)
}
$ go build -gcflags "-S"
"".main STEXT size=139 args=0x0 locals=0x20 funcid=0x0 align=0x0
# 逃逸到堆上的y
LEAQ type.int(SB), AX
CALL runtime.newobject(SB)
AX, "".&y+16(SP)
$222, (AX)
# 打包目标函数和参数
LEAQ type.noalg.struct { F uintptr; ""..autotmp_2 int; ""..autotmp_3 *int }(SB), AX
CALL runtime.newobject(SB)
# funcval.fn --> func1 --> test
LEAQ "".main.func1(SB), CX
MOVQ CX, (AX)
# funcval.x
MOVQ $111, 8(AX)
# funcval.p -> &y
MOVQ "".&y+16(SP), CX
MOVQ CX, 16(AX)
CALL runtime.newproc(SB)
"".main.func1 STEXT size=76 args=0x0 locals=0x18 funcid=0x15 align=0x0
MOVQ 16(DX), BX
MOVQ 8(DX), AX
CALL "".test(SB)
"".test STEXT size=113 args=0x10 locals=0x20 funcid=0x0 align=0x0
# x
MOVQ AX, ""..autotmp_3+16(SP)
# *p
MOVQ (BX), CX
MOVQ CX, ""..autotmp_4+8(SP)
MOVQ ""..autotmp_3+16(SP), AX
CALL runtime.printint(SB)
MOVQ ""..autotmp_4+8(SP), AX
CALL runtime.printint(SB)
了解打包流程后,如下代码就好理解了。
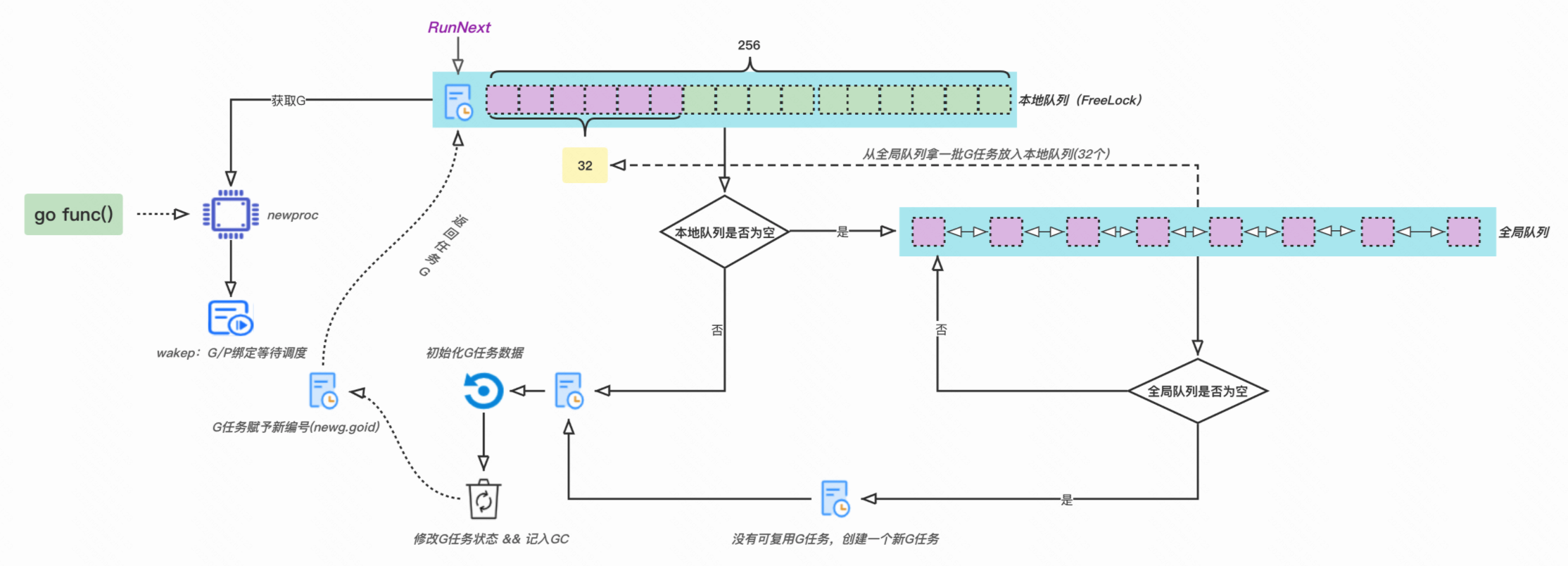
// runtime2.go
type funcval struct {
fn uintptr
// variable-size, fn-specific data here
}
// proc.go
// Create a new g running fn.
// Put it on the queue of g's waiting to run.
// The compiler turns a go statement into a call to this.
func newproc(fn *funcval) {
gp := getg()
// 获取 go func 下一条指令位置。
pc := getcallerpc()
systemstack(func() {
newg := newproc1(fn, gp, pc)
// 获取的g放入本地队列。
_p_ := getg().m.p.ptr()
runqput(_p_, newg, true)
// 如果 main G 启动完毕,则唤醒其他MP执行任务
if mainStarted {
wakep()
}
})
}
取一个G对象(复用或新建),初始化自带栈,并在sched等字段内记录执行相关信息。
// runtime2.go
type g struct {
stack stack
sched gobuf
gopc uintptr // pc of go statement that created this goroutine
startpc uintptr // pc of goroutine function
}
// proc.go
// Create a new g in state _Grunnable, starting at fn. callerpc is the
// address of the go statement that created this. The caller is responsible
// for adding the new g to the scheduler.
func newproc1(fn *funcval, callergp *g, callerpc uintptr) *g {
// 获取可复用 G, 或新建
newg := gfget(_p_)
if newg == nil {
// 本地队列和全局队列都为空,则创建新 G
newg = malg(_StackMin)
casgstatus(newg, _Gidle, _Gdead)
allgadd(newg)
}
// 初始化任务数据
totalSize := uintptr(4*goarch.PtrSize + sys.MinFrameSize) // extra space in case of reads slightly beyond frame
totalSize = alignUp(totalSize, sys.StackAlign)
sp := newg.stack.hi - totalSize
memclrNoHeapPointers(unsafe.Pointer(&newg.sched), unsafe.Sizeof(newg.sched))
newg.sched.sp = sp
newg.stktopsp = sp
newg.sched.pc = abi.FuncPCABI0(goexit) + sys.PCQuantum // +PCQuantum so that previous instruction is in same function
newg.sched.g = guintptr(unsafe.Pointer(newg))
gostartcallfn(&newg.sched, fn)
newg.gopc = callerpc
newg.startpc = fn.fn
// 修改状态,并记录 GC
casgstatus(newg, _Gdead, _Grunnable)
gcController.addScannableStack(_p_, int64(newg.stack.hi-newg.stack.lo))
return newg
}
编号
在sched里有个计数器,用于分配G.goid编号。
// runtime2.go
type schedt struct {
goidgen uint64
}
考虑到多个P共同使用,所以每次都提取一段“缓存”到本地。
// proc.go
// Number of goroutine ids to grab from sched.goidgen to local per-P cache at once.
// 16 seems to provide enough amortization, but other than that it's mostly arbitrary number.
_GoidCacheBatch = 16
// runtime2.go
type p struct {
// Cache of goroutine ids, amortizes accesses to runtime·sched.goidgen.
goidcache uint64
goidcacheend uint64
}
type g struct {
goid int64
}
在newproc1里,通过判断本地计数是否达到尾部(goidcacheend)来决定是否新取一批过来。
就是简单的将 sched.goidgen + 16,表示取走 16 个连续号。这样就保证了多个P之间G.id的唯一性。
注意,G对象复用时,会重新赋予id。通过编号,我们大概能判断进程里共计创建过多个任务。
// proc.go
func newproc1(fn *funcval, callergp *g, callerpc uintptr) *g {
// 复用或新建
newg := gfget(_p_)
if newg == nil {
newg = malg(_StackMin)
casgstatus(newg, _Gidle, _Gdead)
allgadd(newg)
}
// 初始化相关属性...
newg.startpc = fn.fn
casgstatus(newg, _Gdead, _Grunnable)
gcController.addScannableStack(_p_, int64(newg.stack.hi-newg.stack.lo))
// 编号缓存不足,从 sched 取一段回来。
if _p_.goidcache == _p_.goidcacheend {
// Sched.goidgen is the last allocated id,
// this batch must be [sched.goidgen+1, sched.goidgen+GoidCacheBatch].
// At startup sched.goidgen=0, so main goroutine receives goid=1.
_p_.goidcache = atomic.Xadd64(&sched.goidgen, _GoidCacheBatch)
_p_.goidcache -= _GoidCacheBatch - 1
_p_.goidcacheend = _p_.goidcache + _GoidCacheBatch
}
/ 赋予新编号。
newg.goid = int64(_p_.goidcache)
_p_.goidcache++
return newg
}